Abstract
Introduction
Axicabtagene citoleucel (axi-cel) is a recently approved, highly effective treatment for relapsed and refractory aggressive B cell lymphomas. It is complicated by the occurrence of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in > 90% of patients (Neelapu, Locke et al. 2017). CRS is characterized by high fevers and elevation in inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and ferritin. It can progress to hypotension and end-organ damage. The clinical distinction between CRS and bacterial infections is virtually impossible. Procalcitonin (PCT) is FDA approved to aid in antibiotic management and stopping antibiotics in sepsis. It has been shown in several studies and meta-analyses to reduce antibiotic exposure without affecting mortality, including patients with cancer (Bouadma, Luyt et al. 2010, Schuetz, Chiappa et al. 2011, Sedef, Kose et al. 2015).
Methods
We sought to evaluate the utility of PCT as an infectious biomarker in patients undergoing commercial treatment with axi-cel. Patient data was collected retrospectively from two institutions and analyzed for clinical and laboratory characteristics, presence of documented infections, and presence and severity of cytokine release syndrome. PCT levels were drawn per the treating team's discretion based on clinical changes (new onset fever, new onset hypotension, requirement of vasopressors, change in level of care).
Results
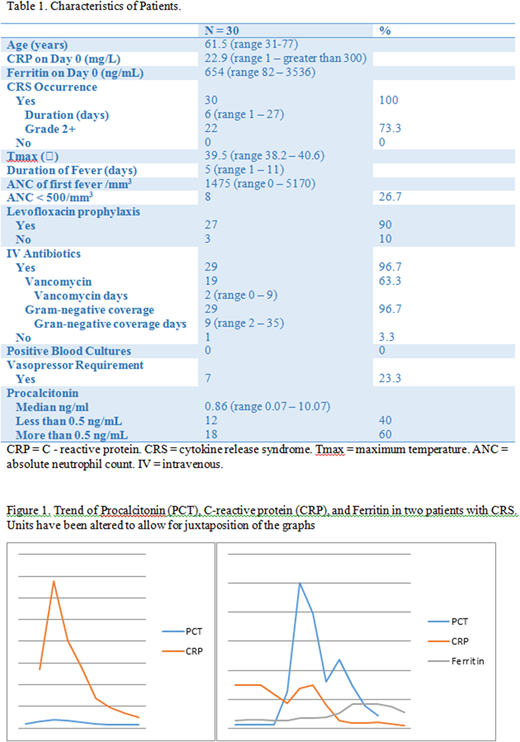
A total of 30 patients received axi-cel for relapsed and refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma and had PCT levels checked during their admission (Table 1). Median age was 61.5 years. Median baseline CRP and ferritin on day of infusion were 22.9 mg/L and 654 ng/mL, respectively. All patients had febrile episodes and evidence of at least grade I CRS by Lee criteria. Median duration of CRS was 6 days. Twenty-two patients (73.3%) had grade 2 or higher CRS. Median maximal temperature was 39.5 0C with a median duration of 5 days. Median number of days till first fever was 1 and median neutrophil count on day of first fever (> 38 0C) was 1475/mm3. Twenty-seven (90%) of the patients were on levofloxacin prophylaxis. Eight patients (26.7%) had an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of less than 500/mm3 on the day of first fever. All but one patient (97%) were started on intravenous antibiotics during their admission. None of the patients had positive blood cultures. One patient had C. difficile infection and one patient had invasive sinusitis with mucormycosis. The timing of these infections did not correspond to the diagnosis of these infections. Median PCT was 0.86 ng/mL. Twelve patients (40%) had values below the cut-off for bacterial infections. Two of these patients required vasopressors. Three patients expired (10%). Two had progressive disease and one had an invasive fungal infection. Figure 1 shows one patient (panel A) who had normal PCT during their CRS episode and another who had abnormal ones.
Discussion
Axi-cel is a novel and promising therapy for treatment of relapsed and refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Therapy is complicated by occurrence of CRS in 94% of patients, which can be fatal if not properly identified and managed. CRS can mimic sepsis and patients are frequently placed on broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics, inducing risk for multi-drug resistant organisms and C. difficile infections. Unlike ferritin and CRP, PCT is typically only elevated in settings of bacterial infections, trauma and surgery and is FDA approved to be utilized in a treatment algorithm for earlier discontinuation of antibiotics in septic patients. It has not been studied in CRS.
PCT was checked per the treating team's discretion and the trend was not followed for most of these patients. We herein hypothesize that PCT does not follow the same kinetics of other inflammatory markers frequently interrogated and may serve as a way to distinguish infection from CRS in this population, where 100% of patients experienced CRS and fevers, but 40% had normal PCT levels. The utility of PCT in antibiotic stewardship and the cut-off of 0.5 ng/mL should be further explored to guide antibiotic use in this population.
Jacobson:Pfizer: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; Humanigen: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Precision Bioscience: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy. Abramson:Merck: Consultancy; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Humanigen: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Verastem: Consultancy. Kline:Merck: Honoraria, Research Funding; iTeos: Research Funding. Cohen:BioInvent: Consultancy; Janssen: Research Funding; Infinity Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Infinity Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millennium: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Millennium: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BioInvent: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Research Funding. Gopal:Teva: Research Funding; Asana: Consultancy; Brim: Consultancy; Aptevo: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Spectrum: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy. Acharya:Teva: Honoraria; Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding. Jaglowski:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Juno: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal